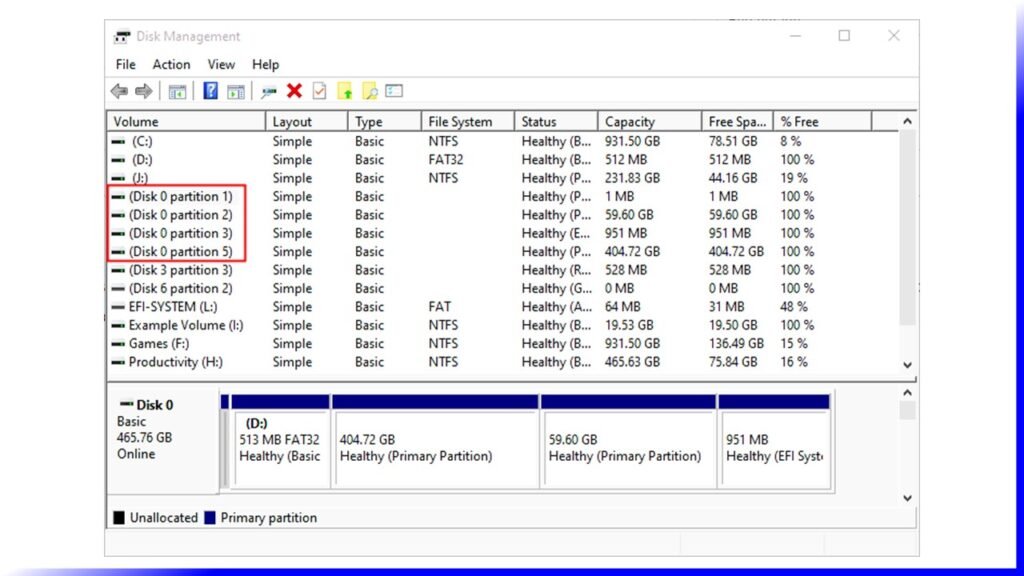
How to create, delete or convert (Logical to Primary) partition drive.

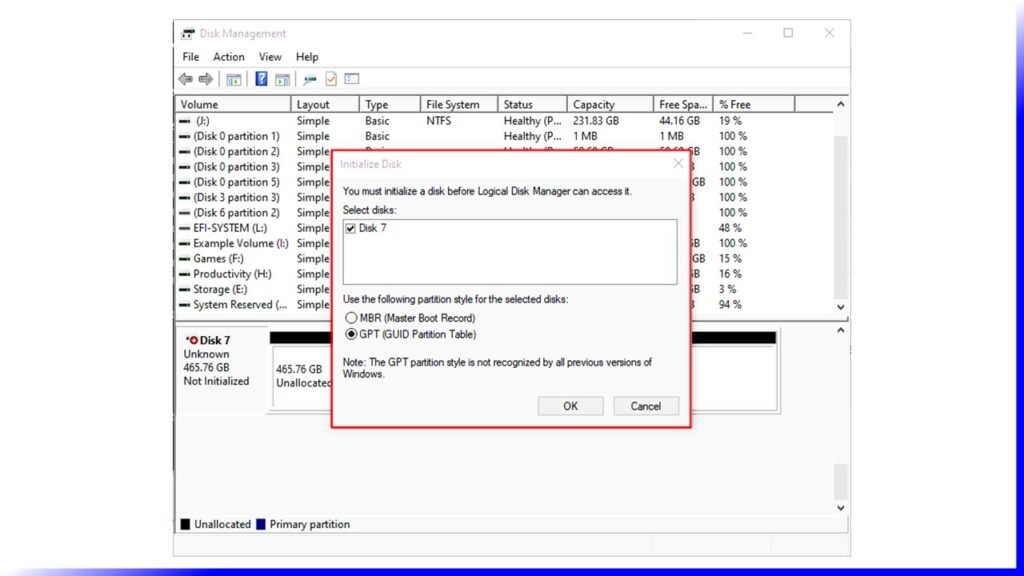
Set up a new disk on Windows 10 or Windows 11, and you’ll be asked whether you want to use MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (GUID Partition Table). Today we’re explaining the difference between GPT and MBR and helping you choose the right one for your PC or Mac.
GPT brings with it many advantages, but MBR is still the most compatible and is still necessary in some cases. This isn’t a Windows-only standard, by the way — macOS, Linux, and other operating systems can also use GPT.
What is a Partition?
A partition just refers to how the space on any kind of storage device — like hard drives, solid state drives, and flash drives — is divided up. Most of the time you only have one partition per drive, but there are plenty of times and cases where you’ll have more than that. Take our “Disk 0,” for example.
A partition structure defines how information is structured on the partition, where partitions begin and end, and also the code that is used during startup if a partition is bootable. If you’ve ever partitioned and formatted a disk — or set up a Mac to dual boot Windows — you’ve likely had to deal with MBR and GPT. GPT is the new standard and is gradually replacing MBR.
On Windows-based PCs, MBR and GPT are two prevalent partitioning techniques. They are layout specifications for storage devices such as an HDD (Hard Disk Drive) or SSD (Solid State Drive). The partition style instructs Windows on accessing the data on the present drive and is selected during disc startup. As a result, having a partition style for each disc in use is required. The partition styles MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) are used to start a hard disc. MBR is the most common format and is compatible with BIOS systems.
GPT is a newer type that works with UEFI systems. MBR maps out the partitions of a hard disc using a table. It may accommodate up to four primary or three primary partitions plus one extended partition. GPT, like MBR, employs a table to map out the partitions on a hard disc, but it does not have the same restrictions. It can accommodate an infinite number of partitions. GPT is also more resistant to corruption and can be retrieved more simply from backups.
GPT (GUID Partition Table) is a partitioning system that stores partition information on a hard disc or another storage device. It is a partitioning strategy alternative to the previous MBR (Master Boot Record) partitioning scheme. To alter a hard drive’s partition style, you must use a partitioning program that supports GPT and MBR. Consider whether your system is BIOS or UEFI when determining which partition style to employ. If it is BIOS, you must use MBR. You can use either MBR or GPT if it’s UEFI.
Read this article to find out more about MBR and GPT Partition and how they are different from each other.
What Do GPT and MBR Do?
You have to partition a disk drive before you can use it. MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) are two different ways of storing the partitioning information on a drive. This information includes where partitions begin and end on the physical disk, so your operating system knows which sectors belong to each partition and which partition is bootable. This is why you have to choose MBR or GPT before creating partitions on a drive.
MBR’s Limitations MBR was first introduced with IBM PC DOS 2.0 in 1983. It’s called Master Boot Record because the MBR is a special boot sector located at the beginning of a drive. This sector contains a boot loader for the installed operating system and information about the drive’s logical partitions. The boot loader is a small bit of code that generally loads the larger boot loader from another partition on a drive. If you have Windows installed, the initial bits of the Windows boot loader reside here — that’s why you may have to repair your MBR if it’s overwritten and Windows won’t start. If you have Linux installed, the GRUB boot loader will typically be located in the MBR.
MBR does have its limitations. For starters, MBR only works with disks up to 2 TB in size. MBR also only supports up to four primary partitions — if you want more, you have to make one of your primary partitions an “extended partition” and create logical partitions inside it. This is a silly little hack and shouldn’t be necessary.
GPT’s Advantages
GPT stands for GUID Partition Table. It’s a new standard that’s gradually replacing MBR. It’s associated with UEFI, which replaces the clunky old BIOS with something more modern. GPT, in turn, replaces the clunky old MBR partitioning system with something more modern. It’s called GUID Partition Table because every partition on your drive has a “globally unique identifier,” or GUID — a random string so long that every GPT partition on earth likely has its own unique identifier.
GPT doesn’t suffer from MBR’s limits. GPT-based drives can be much larger, with size limits dependent on the operating system and its file systems. GPT also allows for a nearly unlimited number of partitions. Again, the limit here will be your operating system — Windows allows up to 128 partitions on a GPT drive, and you don’t have to create an extended partition to make them work.
On an MBR disk, the partitioning and boot data is stored in one place. If this data is overwritten or corrupted, you’re in trouble. In contrast, GPT stores multiple copies of this data across the disk, so it’s much more robust and can recover if the data is corrupted.
GPT also stores cyclic redundancy check (CRC) values to check that its data is intact. If the data is corrupted, GPT can notice the problem and attempt to recover the damaged data from another location on the disk. MBR had no way of knowing if its data was corrupted — you’d only see there was a problem when the boot process failed or your drive’s partitions vanished.
Compatibility
GPT drives tend to include a “protective MBR.” This type of MBR says that the GPT drive has a single partition that extends across the entire drive. If you try to manage a GPT disk with an old tool that can only read MBRs, it will see a single partition that extends across the entire drive. This protective MBR ensures the old tools won’t mistake the GPT drive for an unpartitioned drive and overwrite its GPT data with a new MBR. In other words, the protective MBR protects the GPT data from being overwritten.
Windows can only boot from GPT on UEFI-based computers running 64-bit versions of Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, Vista, and corresponding server versions. All versions of Windows — 11, 10, 8, 7, and Vista — can read GPT drives and use them for data — they just can’t boot from them without UEFI.
What is an MBR partition?
Because of their history, MBR discs function with most Windows editions, particularly earlier ones. Given that, deciding whether GPT or MBR is superior should be based on your needs and the hardware you have. For example, if you desire a faster boot time, use a GPT disc as the system disc; if your computer is BIOS-based, use MBR for the system disc instead; and if you use a disc under 2TB for data storage, both GPT and MBR are acceptable.
MBR, or Master Boot Record, is an older disc format that debuted with IBM PC DOS 2.0 in 1983. It is named after the MBR boot sector, positioned at the beginning of a disc (the first sector). A simplified construction of an MBR disc is shown below.
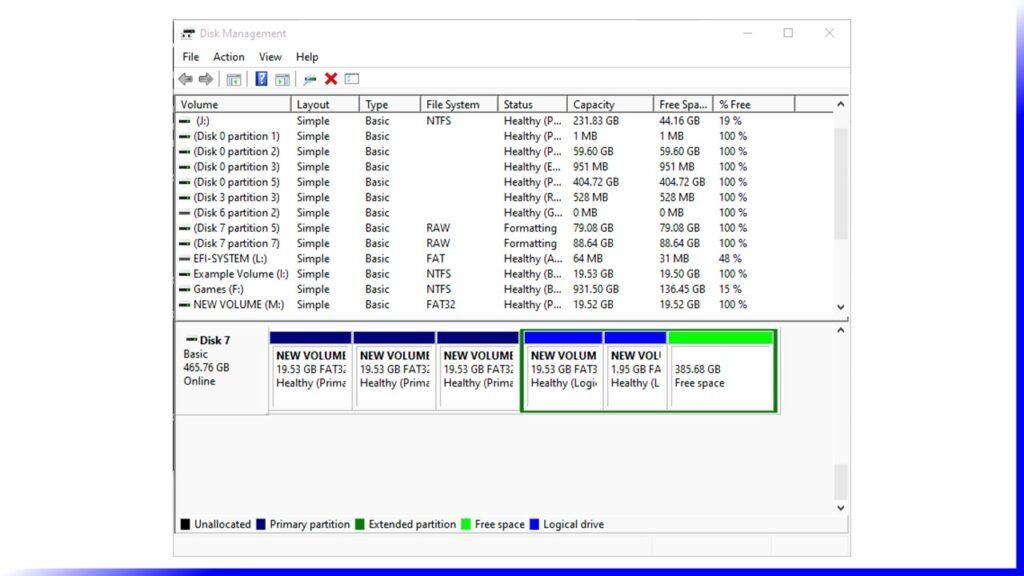
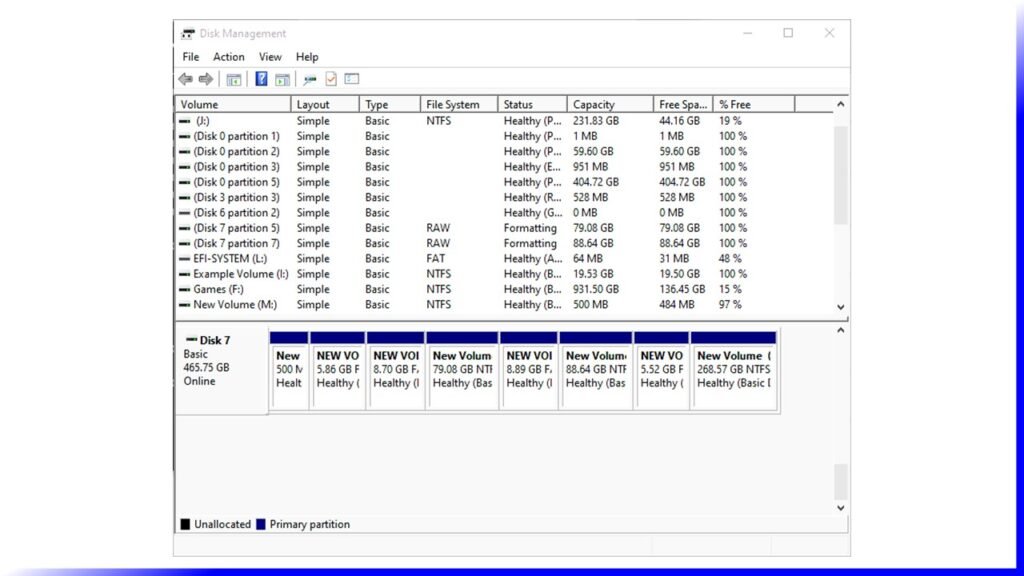
To use a disc for data storage, divide it into parts known as partitions. On an MBR disc, partitions are divided into two types: main and extended. Primary partitions are those on which you may install the operating system and activate it to boot the machine. Excluding primary partitions, the remaining space on a disc is referred to as an extended partition.
Unlike a primary partition, an extended partition is a storage unit that can only be used to build several logical drives or partitions, and it lacks a drive letter and a file system. It functions more like a container for one or more logical partitions with driver letters and file systems.
Because the disc partition table is 64 bytes and each partition’s information is 16, you can only construct four primary partitions. If you want more than four partitions on the drive, make one of the primary partitions an extended partition to generate logical partitions. The most obvious drawback of an MBR disc is that it only supports a maximum disc capacity of 2TB (2TB). If you have a disc larger than 2TB and use the MBR partition format, you can only use 2TB of it.
What is GPT Partition?
GPT, or GUID Partition Table, is a newer standard that replaced MBR, initially presented as part of the UEFI program. Compared to the MBR partitioning system, it is more versatile and compatible with contemporary hardware.
The primary GUID partition table header is stored in the second sector of a GPT disc. It specifies the location and size of the partition entries that comprise the partition table and the cyclic redundancy check (CRC32) checksum required to validate the GPT header’s integrity. When CRC detects data corruption, it will attempt to restore the data by utilizing backups saved at the disk’s end.
GPT discs are more secure and trustworthy than MBR discs. These backups will be useful in restoring data if the GPT header or partition table is damaged. The limitations of MBR do not constrain GPT. GPT-based drives can be substantially bigger, with size restrictions imposed by the operating system and file systems. GPT also supports a practically infinite number of partitions.
The following table highlights the major differences between MBR and GPT Partition
|
Characteristics |
MBR |
GPT |
|---|---|---|
|
Definition |
MBR (Master Boot Record) is a type of partition used to set up a hard disc. |
GPT is crucial to comprehend whether to construct a new division or convert an old one. |
|
Compatibility |
MBR is the most common format and is compatible with BIOS systems. |
GPT is a newer type that works with UEFI systems. |
|
Limitation |
MBR may accommodate up to four primary or three primary partitions plus one extended partition. |
GPT can accommodate an infinite number of partitions. |
|
System types |
If the system is BIOS, we can use Master Board Record. |
If the system is UEFI, we can use either MBR or GPT. |
|
Complexity |
MBR is less complex than GPT |
GPT is also more complex than MBR and works with all operating systems. |
If you need any software support for hard drive partition, You can buy this product.
How to create, delete or convert (Logical to Primary) partition drive.
MiniTool Partition Wizard – Apple Computers
https://applecomputerspk.com/product/minitool-partition-wizard/

